By Boris Zlotin and Alla Zusman
This case study elaborates upon the principles and processes described in "Instruments for Designing Consummate Systems."
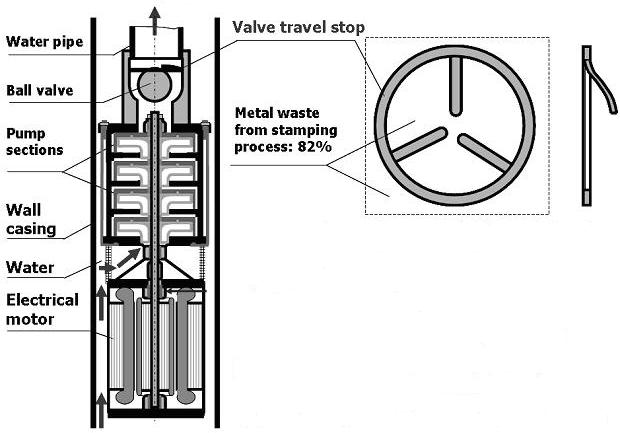
Consider the system of a centrifugal wall pump shown in Figure 1 and of its valve travel stop specifically. The useful functions of the valve travel stop include:
- Allows water to pass through (main function)
- Keeps ball from flowing with water (main function)
- Positions ball in the center of water flow (auxiliary function)
- Positions the valve travel stop in the correct location inside the pump (auxiliary function)
Meanwhile, the system's (valve travel stop's) harmful functions include:
- Thick metal required to prevent destruction of prongs by impact of ball
- Metal waste from stamping process is about 82 percent
| Figure 1: Centrifugal Well Pump |
|  |
|
|
Figure 2 shows the main elements of a valve travel stop.
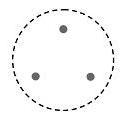
The valve travel stop in Figure 3 has three dots. The dots represent its useful functions. The problem is what is the best way to connect those three dots? With a triangle as seen in Figure 4.
| Figure 3: Ideal Final Result |
|  |
|
|
The new, triangle design (Figure 5) provides one significant benefit for the valve travel stop – the stronger resistance against the impact of the ball allows the thickness of the travel stop to be reduced by a factor of 2. As good as that is, the new travel stop's sharp edges can damage the ball. The new design has led to a secondary issue (Figure 6) – prevent the sharp edges from damaging the ball.
| Figure 6: Secondary Problem |
|  |
|
|
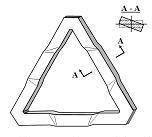
What is the ideal solution for the new design? The sharp edges of the travel stop cannot damage the ball. There is a contradiction in this secondary problem: the travel stop should contact the ball to prevent it from flowing with the water AND it should not contact the ball so that the sharp edges do not damage the ball. How can this contradiction be resolved? Use "separation in space" – the ball should contact the sides of the triangle and not the corners. This is possible if the sides are bent, as shown in Figure 7.
If the sides are bent in the stamping process, then the following benefits are seen:
- Sharp edges of the travel stop cannot contact the ball
- Shape of travel stop is more rigid, providing increased resistance against impact of the ball
- Reduced hydraulic resistance of the water flow
With this solution, there is a new secondary problem – how to save labor and and material?
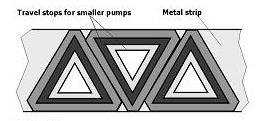
Figure 8's stamping layout shows some additional ideas: 1) stamp travel stops from a metal strip to optimize metal utilization and 2) stamp travel stops for different sizes of pumps simultaneously. The benefit of this layout is material and labor economy.
| Figure 7: Bent Strips Design |
|  |
|
|
| Figure 8: Stamping Layout |
|  |
|
|
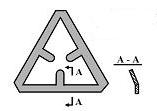
As so often, this solution leads to another secondary problem: for the smallest travel stop (Figure 9), manufacturing tests showed it was impossible to bend the sides without causing metal damage in the corners. The ideal solution? Bend without damage. The contradiction? Sides of the travel stop should be bent to provide protection of the ball AND should not be bent in order to prevent damage to the metal. The contradiction can be resolved by using space resources – it is possible to add a supplementary material to the travel stop and then bend the supplementary material (Figure 10).
| Figure 10: Additional Idea |
|  |
|
|
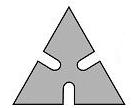
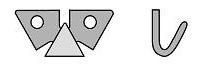
The next secondary problem is seen in Figure 11 – how can the waste be utilized? Figure 12 shows one possible solution – produce a furniture hook with the waste.
| Figure 11: Stamping Waste |
|  |
|
|
| Figure 12: Using the Waste |
|  |
|
|
During three years, three TRIZ specialists and technicians have worked on a centrifugal well pump shown in Figure 13. The work included:
- Obtaining a set of promising directions in building the next generation of pumps.
- Failure analysis for the pumps that revealed more than 20 reasons for the deterioration of reliability and durability of pumps.
- TRIZ-based cost reduction.
| Figure 13: Centrifugal Well Pump Idealization |
|  |
|
|
More than 200 various technological problems related to design and manufacturing process have been addressed resulting in significant quality improvement and production cost reduction.
About the Authors:
Boris Zlotin received his MS in electrical engineering from St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Russia. He has more than 30 years of experience in TRIZ, is widely recognized in the TRIZ community and considered one of the foremost theorists and TRIZ scientists in the world. He is responsible for the majority of the advances made to the methodology to date. He facilitated solving of thousands of various problems, is the author or co-author of 15 books on TRIZ and several patents, and has conducted numerous seminars, workshops, and lectures. Mr. Zlotin is the Chief scientist and VP at Ideation International Inc. Contact Boris Zlotin at azusman12 (at) ideationtriz.com or visit http://www.ideationtriz.com.
Alla Zusman received her MS in radio physics from St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Russia. She has more than 14 years of experience in corporate R&D and over 25 years of experience as a TRIZ expert with patent education. She is one of the main contributors to the development of TRIZ applications - specifically to ARIZ, the patterns of systems evolution, AFD and DE methodologies, and the TRIZSoft® family of software. She is the author or co-author of 14 books on TRIZ and several patents, and has conducted numerous seminars, workshops, and lectures. Ms. Zusman is the Director of TRIZ products development at Ideation International Inc. Contact Alla Zusman at azusman12 (at) ideationtriz.com or visit http://www.ideationtriz.com.
Copyright © 2006-2011
– RealInnovation.com, CTQ Media. All Rights Reserved
Reproduction Without Permission Is Strictly Prohibited –
Request Permission
Publish an Article: Do you have a innovation
tip, learning or case study?
Share it
with the largest community of Innovation
professionals, and be recognized by your peers.
It's a
great way to promote your expertise and/or build your resume.
Read more about submitting an article.