Размещено на сайте 06.02.2009.
Good afternoon, dear readers!
In our previous review dated of January, 10 we published review of materials on diversionary analysis which was suggested to use by TRIZ master, professor Kynin for perfection of forecast instruments in technique development.
Review on diversionary analysis (DA) which was published last Thursday by forecasts department, showed that DA is a methodological principle of high universality level and has great opportunities for further development.
In 1991 Boris Zolotin, author of DA suggested to consider any system in different existence conditions: from projecting to recycling. To this very characteristic of all systems to have different drawbacks in different conditions of existence process - today’s model is devoted.
Prepared material is the response to A.T.Kynin’s suggestion to move in the direction of forecast instruments perfection as well as by method of combination and development of already existent and by mean of creation of absolutely new ideas.
I wish you nice reading.
Rubric leader of “forecasts department” Y. Danilovskiy.
“Diversionary analysis of B.Zolotin” and “harmful machine of V. Lenyashin” or 12 useful questions for building forecast solutions.
Part 1
Y. Danilovskiy
Published at http://www.metodolog.ru/01289/01289.html
Instead of epigraph.
Scientific discoveries of Mozhaiskiy are very important because they ruined old ideas based on wrong hypotheses of Newton. Mozhaiskiy denied obsolescent theories and presented himself as a courageous innovator, real scientist, as a representative of the science about which comrade Stalin said: “Science is called science because it doesn’t recognize fetishes; it is not afraid of ruining everything obsolescent, old and is always sensitive to the voice of experience and practice.”(V.Y.Krylov “Alexander Fyodorovich Mozhaiskiy” L.: Molodaya Gvardiya, 1951.)
Project “Military literature”. The book is at the site www.militera.lib.ru/bio/krylov/index.html
Plan
1 two main ideas of DA method.
2 one more important idea of Harmful Machine Method. (HM).
3 synthesis of two methods.
4 example of considering of two systems in the format of consumption cycle.
5 example of 12 questions in the format of consumption cycle for a certain system.
6 example of the use of the format cycle in forecast investigations.
7 possible directions of forecast instruments development.
8 conclusion.
- Two main ideas of DA method.
The first important idea
Diversionary analysis, as it seems to me, has a deeper idea than a simple methodological construction of formulating questions, the answers to which are capable to improve the machine under study.
The majority of our readers know well the formula of invention described by famous French poet Paul Valery: “to invent something you must be in two faces. One makes combinations, the other chooses what corresponds with his wish and what he considers important in the things the first invented.” Agree that the second who makes a choice makes a procedure of mental experiments in drawback search.
So it means that the first in the pair formulates suggestions about the system change in the direction of its improvement, the second make a mental experiment – diversion towards just appeared system.
If diversion is a success the suggestion is ignored, if not, then it is given further consideration.
DA approach popularity illustrated in the previous FD review can be explained by the fact this methodology is used unconsciously in the block of mental procedures of technical or organizational creativity.
A special merit of B. Zolotin is that he verbalized this procedure, gave it a separate name and made it understandable for everyone who knew about this for the first time.
The second important idea
The first participant of invention process, according to Valery formula, can use in his algorithm knowledges of technique development laws and can not use them. The second one who thinks of diversions doesn’t necessarily use these knowledges if diversions are not fantastic but real, taken from the experience of real failures of ever made machines.
Conclusion 2
Block of knowledges about failures or in special terminology, diversions, is also important as well as a block of knowledges about fortunes so it means about the script of successful existence of a novelty or technique development laws.
2 One more important idea of harmful machine (HM) method.
Let’s study in brief harmful machine model described in the article “Harmful System” by V.A.Lenyashine [4].
I’ll notice that it would be more convenient to say not a harmful system (HS) but harmful machine. Author does this in his work explaining the use of this word by goal-oriented allusions to general philosophical mechanistic understanding of systems. I also like this word phrase because it lets not enter the zone of psychological inertia connected with the historical heritage of TRIZ.
The lack of context in this article perceived as: not a single independent action as it is sometimes interpreted in TRIZ literature but as something that manifests itself as an action accompanying the main one…” So any system is considered by V.Lenyashin as a compulsory simultaneous existence of two machines, :useful and harmful” and a process of improvement of “a useful one” is resulted to “diversion” organization for “a harmful one” by the same apparatus means which we use in the analysis practice and we name it LDTS (Laws of development of technical systems).

Strongly simplifying we can say the following:
We determine HM and destroy it with the help of diversion and we use all LDTS instruments in the form of “logical illusion”.
Example: in one of the main LDTS statements about “through pass of energy” necessary and satisfactory condition of minimal system working capacity in the form of “energy flow continuity” is formulated but for “diversion” in relation to “harmful machine” “discontinuity” must be made.
It is really an old idea glimpsed in LDTS GEN3 course [4а] but glimpsed as one phrase: “Consequently it was found out that systems development goes not only by means of increase of useful flows conductivity but by means of reduce of harmful and parasitic ones. For this aim there are special mechanisms (often reflection symmetric to mechanisms of increase of useful flows conductivity)…”
It’s stupid to talk about priorities of superiority even if this course was closed for ordinary readers for a long time. The date of its open publishing – 2006, year of its writing – 2002 when I studied it in the capacity of GEN3 recruit. The majority of Lenyashin’s works had the same status though the HM model was not known to me from Lenyashin himself. In 2001we worked together over my and teachers’ projects of that period. This is not a secret for anyone.
Method that Lenyashin formulates is logically proved: things that are good for useful machine can be used for destroying a harmful one, if make a procedure of opposite idea:
to replace through pass of energy to discontinuity. Roughly speaking to use LDTS knowledge for diversion building. Though to make everything vice versa LDTS recommendations. On the way I’d like to remind you that Zolotin has “list of 5” in the form of “typical mistakes in TS development”, deviation situations from LDTS scripts. These deviations are not obligatory opposite in the idea that’s why LDTS use by Zolotin and Lenyashin is not the same.
We can illustrate the result of application of such method with a simple example: presence of electrical insulation on pliers (through pass of electrical energy is prevented in case of striking people with current) or ergonomic form of this insulation ( form of handles agrees to finger form).
In the first case diversion for HM is created in the form of current capable to affect a man, in the second case diversion is created for harmful effect of mechanical field: (diversion: increased the surface area.)
Conclusion 1
If we come back to Paul Valerie formula then the first participant of the invention process finds out a harmful machine, the second participant, using “LDTS logical illusion”, makes diversion. Thank to this a new technical solution appears.
This is the very important idea to which I’d like to pay readers attention to use this concept in further synthesis of two effective methods.
Notice
DA and HM also give identical result – new variant of technical system which is received with the help of diversion building and knowledge about technique development laws. They are relative but different.
Synthesis of two methods
If we sum up briefly all said in first two points then the following table will let understand that DA and HM methods give the same result but by different means.
| Methods of systems improvement | First participant | Second participant | Result |
| DA | Offers combinations and studies consumption cycle | Makes diversions in relation to the offered “searches” HM |
Improved operable system |
| HM | Finds out harmful machines | Uses LDTS logical illusion for HM destroy | Improved operable system |
I can say that these means are based upon stages contradicting from the point of view of sequence, for example finding out HM.
V.Lenyashin studies it on the first stage and destroys it with the help of “LDTS logical illusion”.
B.Zolotin lays out a system into consumption cycle from projecting to recycling and on every stage makes mental operations on verification on the base of “typical mistakes in development” list. For this aim he describes the structure technique development laws itself and compares it with most frequent examples of ignoring by developers, producers and sellers of scripts of machine successful existence (LDTS).
Upon all said above synthesis of two methods is possible.
From DA we can take the idea of “expanding a machine to series” to the stages of its existence having changed the consequence – projecting, production, exploitation, repair, recycling to another: 1) acquire, 2) learnt, 3) got, 4) switched on, 5) work on, 6) have a minute break, 7) used additional systems (if it’s necessary), 8) filled in, 9)fold (to take with you and carry in a pocket, bag, boot), 10) take (suffer transport affects, break, spoil), 11) repaired, 12) pay for recycling.
WE USE ONLY VERBS ON PURPOSE to see the “action”.
Notice
Don’t take literally this sequence as a technological step by step stage of consumption.
For example, situation “repaired” can appear on the stage “learnt” or “got”. Drop just bought telephone on a tile floor. If the case is easy to change then this is the one stage of system development; if it is impossible then the stage “recycling” immediately appears. The offered model is just only a variation of a flow chart in which the most of typical for machine phases are reflected.
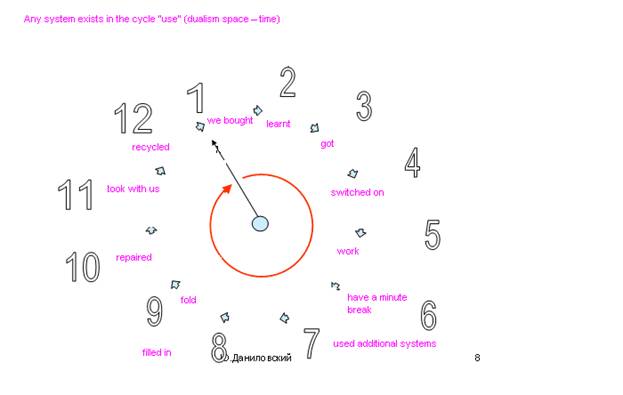
To the term “machine” on this stage it is good to add new ideas, first of all marketing and marketological categories together with general technical categories.
Modern TRIZ is developing on the way of adding to technical models the arsenal of marketing specialists’ methods. The fact that classical TRIZ used in its studies market phenomena in the technique development unwittingly and fragmentarily, for example, “cheap fragility” or “color change” was a drawback which is removing systematically by the procedures: TRIZ + FCA, MPV Analysis (Main Parameters of Value Analysis), method of quality function design (QFD) and bench marketing [5] and other analytical instruments of modern TRIZ and GEN3 Innovation Discipline [6]
Let’s use perception of a drawback as a “machine” offered by Lenyashin, “machine” with all its specific characteristics of classical TRIZ model: working head, transmission, engine, energy source and control system. Two last elements can be in sub system. In further discussions let’s remember that any machine has parts or functionally different blocks. This understanding gives us the possibility to look foe at least 5 Harmful Machines on the number of functional blocks.
“Diversion” approaches in relation to “harmful machine” will be done in the same way as Lenyashin’s but only 12 times on the number of separated consumption phases.
The main idea of presented model of consumption cycle is very simple, isn’t it? There are 12 stages of consumption cycle and on every stage we look for HM and make “diversion” receiving in this way 12 new machine variants and we move in the direction of removing drawbacks.
4 Example of study of two systems in the format of consumption cycle
Historically practice of TRIZ – analyses traditionally divides objects under research into “technical systems” and “technologies”. Both pencil and “fetish of our modern civilization”, mobile telephone, are also “technologies” if we see the process of use in the form of consumption phases. Pencil doesn’t exist on its own. The process of its use can be seen as the technology of making information.
Think yourself. To use a pen and get a product it was created for we can easily sea a certain quantity of obligatory stages which are specific to a pen or to any other “machine”.
First you must “buy” it. This phase we’ll leave for some time because the “diversions” for “harmful machines” are so various and sometimes so specific that’s why this stage must be specially marked out and we’ll study this material in the end of description of all consumption phases.
The first thing we must do after “getting” is to examine the device and study an instruction for it.
These are also expenses of both a consumer and a producer.
A producer must spend on instruction making and a consumer must spend his time on studying it so “understanding” is one of “price” segment and it’s better to say “cost after buying”.
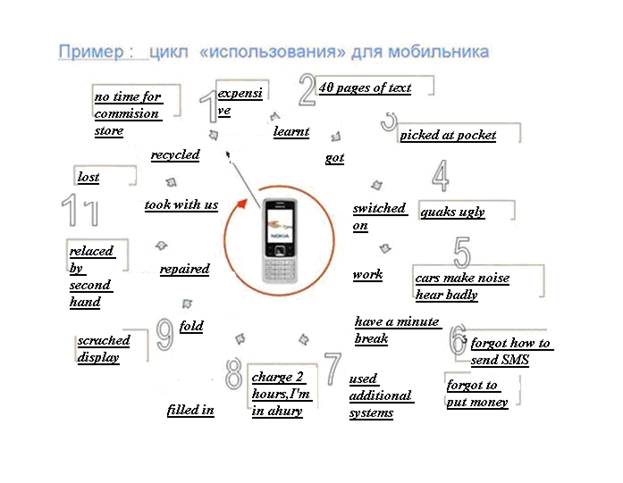
Expenses can either be absent (pencil) or great if we compare different gadget models. In Nokia models interface is primitive built on circular like graphs.
Other producers’ interface is not simple, tree –like and it takes time to remember. One of my gadgets illustrates this. This is Ubiquam model.
That’s why I use 2 gadgets. From Nokia I make dialed calls because it is comfortable and I use Ubiquam for replying incoming calls and the main purpose of the model is Internet because it is cheaper in this company. But if this machine didn’t puzzle me with all 8 procedures I must do to open a notebook and what I always forget would I buy an old Nokia then? I am not the most stupid user but this situation is more convenient for me and I surely know that my decision to have 2 gadgets is not amazing.
Two diagrams are presented below. They are made in the form a clock which is used to lean to see in any thing first of all a “technology”.
Moreover any machine has a certain additional well distinguished set of “expenses”9time for understanding, mussel energy, number of movements, money on expendable materials and etc.) which are negative activity products for example of a gadget or a pencil.
It’s curious that in the use of a pencil the “understanding” phase is absent but for one of collection pens much time is spent.
We can guess that the outlet of one or the other writing organ is connected with the field of gravity. Every turning of this pen in a horizontal plane for 45 degrees gives either a pencil or a gel pen or other useful devices such as a highlighter or “a pin” for touchpad management.
Additional notice
The thing that Lenyashin called “a harmful machine” which doesn’t seem to exist because it is “ideal”is described by certain and measured parameters. It means that HM can be “measured” and “classified” . Let’s study it further.
Further I have a great wish to ask myself 11 times only one question of “diversion analysis”: “What must I do to break it?” I’ll remind that the object of application of this analysis is not “a machine” itself but these very virtual 11 HM.
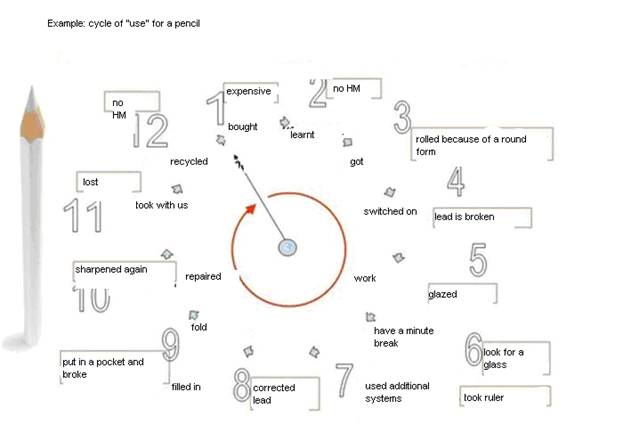
Let’s study the example of the chosen model use to describe changes in such a well known system as a pencil or a pen.
I’ll remind once again that “banality of illustrating examples” is apparent. Everything develops from simple to complicate. Only having studied a new methodic on simple samples you will feel yourself sure in a more complicated material.
“Clock-face of machine use phases” model gives us a simple graph with 12 lines (or “force lines” not to limit imagination) along which you can make variants of a certain machine development and which we can interpret as 12 questions necessary for getting answers in the form of future machines images.
5 Examples of 12 questions the format of consumption cycle for a certain system.
We remember that the first question about HM while selling we’ll postpone for the end that’s why let’s study the rest 11consumption phases first.


The problem of interpretation of this or that solution is not always simple because every phenomenon has not only one “method” or “law’. Examples in the table can be replaced by others. Moreover each of them can illustrate with equal success an answer for any other question from the list above.
So I line 12 I placed an answer zone “how to destroy (reduce) expenses on recycling a pencil for example though it can be an answer for question 8 “how to destroy expenses on filling in”. For a pencil this is a sharpening.
Important characteristic of HM method is presentation of a drawback in the form of a machine with all model specifications. Asking a question in the format chosen we must remember that HM has 5 parts and in each we can make a diversion.
For example in the question 12 about “recycling cost”, HM product (in theory) is “quantity of energy spent for recycling of a worked – out car”.
In relation of a pencil all these speculations are absolutely imaginary. They are used to illustrate the work of method. Diversion of a HM in this situation is made for “energy resource” necessary for recycling of an old worked out its resource machine. Let’s replace the material of timber by paper and we’ll get another (less) parameters of recycling energy resource.
We clearly understand that nobody recycles pencil stubs either paper or wooden. However the problem of Hg fluorescent lamp recycling is not easy and their degree of efficiency is very high after including demercurization costs (this is my personal hypothesis) can give quite unexpected total opinion. These lamps are less profitable than incandescent lamps. There the problem is not “theoretical”.
An important quality of HM method is that in a machine there are 5 parts as in any machine and for every of which we can make a diversion. You mustn’t understand this as “did once, do twice”. It is not very good for mental procedures as well as the use of a model of technical contradiction are not always reasonable and easily determined.
Nevertheless the ideas to study HM as a model of 5 parts are quite real.
For example in question 9 “how to remove the default of a small dimension after addition”. The solution is either a hinge or “matryoshka”.
HM in this situation is not a “small dimension” but an ergonomic discomfort which a pencil has for its holding.
Simply speaking the body of a pencil is a transmission according to a TC model. It is also a transmission to a HM. Contradicting demands are made to the body: it must be little for carrying” and big enough for comfortable writing. Well known law “agreement/disagreement” is dualistic in its meaning and has “logical illusion” inside which is based upon HM method.
To HM machine transmission we make the same contradicting demands. While carrying diversion for HM – “small body” (operation with transmission) disagreement of transport affects on the body which we have because we minified line dimensions of a body.
While using HM – disagreement of transmission line dimensions and man hand dimensions. Diversion in the transmission zone is agreement of body line dimensions and ergonomic parameters.
As a matter of fact this tiring passage wouldn’t be necessary if while preparing materials there were not so many doubts in genetic relationship between the presented model of consumption cycles DA and NH. Nevertheless it exists and there is no reason to deny it and this whole explanation block was devoted to it.
For every consumption phase discussed many examples can be given. My collection* of “these machines” which I began in 2001can give dozens of examples of “answers” for every question.
The first question in a collaborated methodic I missed because there are so many answers for it and it needs more detailed analyses. The volume of this collection is great (500 samples) and the biggest part of them (400) answers this very question: “what must we do to destroy HM on reducing quantity of sales?” or to paraphrase this “what must we do surprise a customer so he gives us a little money?”
There are many goods in the market. Everybody tries to create new parameters trying to make consuming qualities of any suggested machine better and willing to increase sales.
We can notice that in the process of machine development two basic mechanisms of formation take part “from technical possibilities” and “from market methods” that I have already begun to speak about.
May be I am mistaken but the best way to sell something new is “to surprise” a customer. If one of the slogans of the war is “veni, vidi, vici” then the slogan of a successful novelty trade is “vini, vidi, bought”. It is possible “to surprise with a price” (it can be either very high or very low).
In this case examples are not necessary. In any range of goods there are very cheap pens and there are pens with the price of a good car. Both phenomena are two poles of obligatory extremes which exist in all goods – giants and dwarfs.
I was really surprised with the price of a pen of 3 cents and I bought it. There are people who buy pens for 7000 $ because they are also “surprised» and the try to surprise other people.
When I compare the act of sale with a famous aphorism of Julius Caesar I speak not only about price but also about “line dimensions”, “producing parameters”, “economic efficiency” and etc.
This problem must be discussed separately and I’ll came back to it later.
It is also possible to surprise with a new specially made and a very simple but making a thing worse “surprising option”.
Look. Is it possible to draw with such a pencil?
This pencil can be tied in a knot, amuse people around or to make a present. Though real “harmful machine” – a broken pencil during transportation exists and it is solved with the whole arsenal of methods “solfeggio of engineering creativity”: from cases, pencil boxes, tips and different “telescopes” to increase of elasticity of the pencil itself by replacement of traditional wood to plastic.
There are great doubts about usefulness of a combination of a pen and …for example a police whistle. And what is the engineering idea?
Changes that must be included in a product are “penny” but the growth of sales will be guaranteed (at least for some time until people are tired of it).
Some word about HM in this situation. In the very beginning of our speculations about HM in the field of sales it was said that that “harmful machine” is a usual set of consumer characteristics. I’ll say this in a different way. Undesirable effect which is overcome by such set of solutions is “reduce of sales number”. There are no logical barriers to line an analogy between the reduce of compression of a car bucket because of its surface exhaustion and the addition of “something” (for example antiwear additive to oil) to break HM.
In this unusual for TRIZ case there are also “reduce” of parameter (number of sales in a unit time) and “addition of new substance”.
When the phenomenon of surprise is over HM appears again. The number of iterations is endless.
Pay attention that one and the same engineering methods can be used both in interests of real “technically supported need”, for example: to make the pen case transparent to know how much ink is left (combination with informational systems) and in the interests of the machine itself “from mammon”, it means to sell with the help of surprising option.

I’ll try to explain this in more details. Satisfaction of really exist needs and creating “surprising options” only for increasing number of sales is supported by one and the same methods.
Example
Tell me, please, dear “normal mentally balanced car drivers” if you need transparent wheel disk from polycarbonate? [7]

Of course not! However fans of a car tuning which is less 1% among drivers will like it.
Both described mechanisms – “from machines (engineering practicality) and from “willing to sell” are created as I have already said by the same means. They are “interlace with each other” as fingers of left and right hands clasped. That’s why “harmful machine” in the form of “they buy pens badly” is solved by the method “combination”. See right and left picture.
The end
*On the way I’ll thank all my friends and relatives who ct contributed in this “global civilization research”: to my mother Nina Archipovna, to my brother Sergey, to my wife Olga, to Voluslav Vladimirovich Mitrofanov, Vasiliy Lenyashin , Alexander Kynin and Mihail Orlov.
Literature used
[1] http://www.metodolog.ru/01282/01282.html
[2] http://www.metodolog.ru/01276/01276.html
[3] http://test.enigma.uran.ru/e-books/book_djvu/adamar/adamar.html
[4] http://www.metodolog.ru/00859/00859.html
[4а] http://www.metodolog.ru/00822/00822.html
[5] http://www.metodolog.ru/00919/00919.html
[6] http://www.expert.ru/printissues/expert/2007/48/innovacionniy_biznes/
Review editor: T. Ryzhkova.
PART 2
“Diversionary analysis of B.Zolotin” and “harmful machine of V. Lenyashin” or 12 useful questions for building forecast solutions.
The end. The beginning in the previous review.
Y. Danilovskiy
6. Examples of cycle format use in forecast research.
Finishing the analysis of 12 consumption cycle phases I’ll tell you in brief about the fact that this approach is productive in my personal experiments.
I’ll remind you its contents which were described in the previous review. It was suggested to study 12 consumption cycle phases: buying, studying the device, learning to use, using, breaks in work, switching on, setting, switching off, transportation, filling in, repairing and recycling.
In every of these phases there are drawbacks which we try to study in the structure “machine” that traditionally has 5 parts. Then we make a diversion for a drawback taken in the format of a harmful machine (HM). In other words this is a kind of change of construction where the drawback is removed completely or reduced. In this way we get 12 variants of changes which can be created in the system under study. It is comfortable to make diversions mentally traveling the laws we know.
It’s reasonable to choose a direction of a movement in changes in the form opposite towards movements recommended by LDTS (laws of engineering systems development). For example, permanence of substance and energy flow must be associated with the break in this flow, transmit monolith – hinge can be associated with transmit hinge – monolith and etc.
However this is not a hard demand as you will see further. It’s possible to use direct LDTS recommendations together with logical illusion.
Remember you mustn’t take this algorithm as strict, proportional and verified receipt. Engineering creativity is not Drill and Ceremonies and is not a production of silicic chips where defect causes fault or catastrophe. It can not be base upon strict algorithms. Here the analogy with chess is a good example, where methods play parts of figures. These methods were got after the investigation of machine characteristics and user – a chess player has a certain idea, strategy and tactics in the use of all figures.
Formulating a drawback in the form of a structure of 5 elements can frequently meet idea difficulties but the orient on a mental search of such structure or method of drawback understanding is useful.
The work of both parts of such a processor is interconnected. One part helps the other. I had to explain the above mentioned examples using the first and the second parts separately just to illustrate its work.
I should notice that the most of the “made up” solutions answer question 1 (about surprising options).
Some colleagues having heard my examples of effectiveness opposed this way: “I saw such a multi-colored pencil in Germany in 1982”. But when I was developing this solution, I couldn’t have known about its existence.
Such kind of reproach, I mean that the forecasting was performed some time ago and not in the presence of everybody, formed the idea of ‘patent paintball’, an activity when the solution is made here and now, ‘right before the audience’. Some time late a manufacturer writes about it in the proceedings of the Forecasting Department. Then nobody may doubt the quality of such an experiment. If the forecaster describes his decision up to the point, his technique is worth it. If not, then …not. You may see why it is rather frightening to take part in such and experiment.
I have simplified my speculations intentionally as we don’t have clear criteria to understand within what limits we should make forecasts. Let’s suppose somebody majors in long – run forecasting. Let’s suppose his solution is described and available for manufacturers but nobody is interested. It isn’t produced, we cannot buy it this year and next year and later. Does it mean that the forecaster must be made fun of? Of course not. I only slightly mentioned here another very important problem which should be developed more thoroughly and which may cause some of our readers replies.
I would also like to mention another example of successful forecasting of technologies development; we may study it in more details in next issues.
In 1991 I used a similar approach to predict the development of fire extinguishing systems. I managed to collect all known systems into one classification so that we could describe all existing and possible machines by means of one formalized formulae.
As a result we obtained a kind of periodical system which allowed us to express all the properties of every fire – extinguishing system in the form similar to chemical formulae.

The morphological chart for generating new solutions in the area of fire extinguishing.
In the left part of the chart you see “The projecting bank of conceptions of fire – extinguishing equipment”. The conceptions are directed to the following main points: 1) reliability; 2) multi-functions; 3) effectiveness; 4) consumer properties; 5) reduction of application hazards;
In the right part you see “The bank of possible technological solutions in each of the parts of the system.
Fifteen years elapsed and in 2006 I took the chart and found a few solutions which had appeared in the recent years. There were only 7 of them, but 15 years is too short a period of time for fire-fighting, which is an extremely conservative area.
I will write about these experiments in more details in one of our following issues as it is quite a bulky story. Working with this chart resulted in about 500 quite patentable ideas of which 50 most interesting were chosen. You could judge how patentable they were from my successful experience of applying for patents since 1986 up to 1991. I got more than 50 certificates of authorship in the area of fire extinguishing, that’s why I know the patent fund quite well, I also studied it thoroughly for 20 years ( in 1970 – 1990) using abstract journals.
7. Possible directions of forecasting techniques development
We are going to study things which belong to a broader area than described in the headline, but I decided not to separate them from Diversion analysis (DA) and the Harmful machine (HM).
How could we further develop the tool part of TRIZ (first of all The Laws of Technical systems development) – if we are based on DA and HM?
Up to now we have been dealing with it by hit of miss method of trying different trends known from ZRTS (The laws of technological systems development). If we know about 20 scripts, we can do about 20 attempts at the task. This way of hit-or-miss application was substituted by an algorithm as in the work by Litvin and Lubomirsky С.Литвина и А.Любомирского [9].
But! The algorithm of ZRTS application, which we can find in [9] has another target, an absolutely different one, to invent, but not to choose the most plausible solution.
Different targets suppose different tools. You can come to the idea that together with ARIZ (which is a system of reasoning for inventing) there must be another technique for selecting the best solutions, a kind of ariz for forecasting, where the noun ARIZ mean ‘engineering philosophy’.
Is is for the good or for the worse? The most suitable answer is: it’s good but incorrect. The algorithm is rather simplistic.
I suggested it only because I made sure in its workability quite a few times and also because I see possible directions for its improving.
Let’s study this subsidiary train of thoughts.
Up to now we have studied vectors of search and finding the developmental trends by drawing analogues to the most frequently occurred changes and scripts of ‘useful’ properties of machines.
All descriptions even were started with the words ‘increasing if dynamism, control, conductivity, agreement/disagreement, fullness of parts, even completeness of sufield relations and ideality «идеальности» [10]
I’d like to add a few word about ideality. The problem is that ‘forecasting TRIZ’ principally can’t use most of models of classical TRIZ; we’ll have to create a detailed explanation work on the differences of these methods. Now I can make only a few brief notes.
You can see it yourselves. If I study the process of unification of functions in this mode в таком формате (it is shown in the diagram below [11]) and the scripts of the diminishing of overheads are in the list following the diagram, I’ll have to remember about 110 scripts of ‘increasing ideality’.
We see eleven varieties of functions multiplied by ten scripts of diminishing of factor of overheads (which is so difficult to measure that the following attempts to increase or decrease ideality bring us to a deadlock). I don’t know how to increase such ideality.
Let’s study the diagram illustrating both the manifestationd of the principle of uniting and the difficulties which we have to face when we use the traditional model of ideality from classical TRIZ.
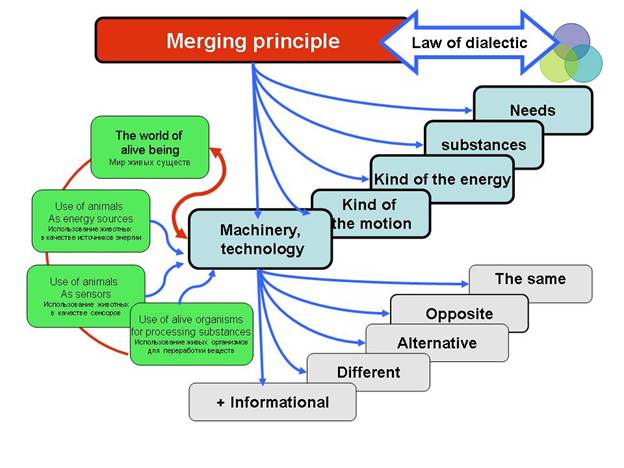
The diagram
In the red box we see the “Principle of unity” which is related to the laws of dialectics. The principle of unity is linked to (left – right) machines, gadgets, technologies, then to the types of movements, kinds of energy, …and substance, needs.
The box “machines, mechanisms and technologies” is linked to the boxes in the area below: informational, different, alternative, opposite, similar.
Under the box “different” we see “similar in cycle’, and ‘4 variants of age’.
The green boxes are: - the world of living things; - use of animals as sources of energy; use of animals as sensors; - use of living things for processing substances;
Nearly all the possibilities of functions unity are illustrated in the collection of my blogg, which was created especially for this purpose. I should remind you again: the differences in ZRTS methods of forecasting and classical TRIZ forecasting are principal and determined by different goals.
The goal of classical TRIZ is to invent. ZRTS forecasting directs us to correctly choose the most plausible technological solutions among the total of obtained ones, the ones which have the best chances to survive. But the first doesn’t reject the second. We need techniques both for engineering creativity and for estimations of its products.
Let’s get back to the problem of ideality, and study possible mechanisms of decreasing prices if we can regard the factor of costs this way.
The mechanisms of lowering of ‘the factor of costs’ with the regard of lowering price
1. Reduction in the number of the parts following the principle ‘sharing functions’ «передать функцию» [12]
2. Use of other substances on the principle ‘metall-plastic’
3. use of the principle ‘disposable goods’ for repeated use of the substance.
4. use of the principle ‘the substitution of a bloke’
5. use of resource of outer fields at the moment of the function performance.
6. use of resource of outer fields before the moment of the function performance
7. use of resource of outer fields after the moment of the function performance
8. use of resources of the environment
9. use of resources of the inner fields (recuperation)
10. use of the space of portable things as a resource
This example demonstrates the fact that ‘inventing tasks’ which we recommend somebody for implementing their ZRTS approaches are so different from inventing that it eventually brings us to constructing absolutely different set of terms and definitions.
As in Newton’s physics for solving tasks in the area of mechanics we don’t need the notion of ‘allowed and forbidden quantum conditions’, in the area of selecting or forecasting TRIZ we can’t use many notions of classical TRIZ. However I should notice something important, that different goals of classical TRIZ forecasting don’t create a conflict as well as having the right and left hands don’t create a problem for a human being.
The materials given in the above mentioned diagram is discussable and it is a hypothesis which we need to discuss in the future. To do this I need to give at least a few explanations regarding the proportion of the categories of ‘the age of the system’ and ‘the unity of systems’, as the block of the diagram ‘the 4 variants of unity of systems according to the age’ needs both explanations and discussions. Explanations are given in my collections of examples «Объединение Старых и Молодых» [13]
Now I should return to the review of possible directions of development of forecasting tools.
Within the area of classical TRIZ, it’s difficult to create a system of knowledge which doesn’t regard the ‘useful properties’, but regards the ‘harmful machines’ which really exist, can be measured and need systematizing as well as a system of useful properties.
While preparing this article we found that an attempt to create a system of harmful effects were made in 1970s in works of Alexandrov, but Interned search for them brought no results. I would appreciate your sharing with me any information on his works.
As a matter of fact, all modern ZRTS systems, from Altshuller’s to Litvin’s, Lubomirsky, Petrov, Salamatov and Polovinkin’s [14] describe time changes in the chosen ‘useful’ properties of systems: dinamisity, agreement/disagreement, fullness, conductivity and so on.
However, we clearly see that while developing one ‘harmful machine’ is substituting another according to the hypothetical law of preserving the balance of usefulness/harmfulness. And as in the case of useful properties, or ‘ZRTS of relatively real machines’, there will be typical scripts which will have the same heuristic value to add to the palette of engineering creativity as well as ZRTS itself, this very ‘machine of empiric observations’.
In this ‘methodological idea’: to set the task of finding of typical scripts of substitution one harmful machine by another, our knowledge will become similar to the model of function of complex variable. There will be the ‘substantial’ part (ZRTS or ZRTS of relatively useful properties) and
‘would be’ part (ZRTS of relatively harmful properties).
Harmful machines can be satisfactorily classified according to the principle “the resource of development”. Here’s an example of such a classification
36 types of harmful machines AND 9 LAWS TRIZ
| substance | field | space (shape) | Time (speed) | Information (need) | Information (price) |
| Harmful substances | Harmful fields (low resistance to harmful disturbances) | Big size while transporting | Low durability (span of life( | NO correcting function | High costs of preparing for manufacture |
| are there consumables | too heavy | too big while stored | takes too long to recharge | can’t be repaired | Too low price is bad too |
| Low productiveness | consumes too much energy | extravagant form | works separately too short time | no mobility | high price is bad |
| Energopumps Low value of the substance |
Takes too much energy when switched on | The shape and form are banal | ergonomy short time before you get tired | little additional functions | high cost of repair |
| necessity to put away substances | takes too much energy to switch | the shape doesn’t correspond to ??? | Low speed the performance is slow | too many additional functions (not reliable) | The consumables are expensive |
| necessity to provide a source of energy or a control unit | too many moving parts | operating span is small | takes too long to master (a difficult machine) | needs additional systems | high price of utilization |


You can see some examples of my work with this system in my blog опыты[15].
This system is a hypothesis which can further be developed in the following direction.
For example you can have a task to make a digital description of a bulky part of history of technologies. This mode of matrix type is good as you can turn any machine in the system of 1 and 0 (if it’s a harmful machine , you put 1, if not – 0). Then every matrix is assigned the parameter of chronology (time) and we get the evolution of technologies in digital format. It will be the history of drawbacks, though.
You can imagine that we have made the digital form of at least 10 families of machines: the story of the vacuum cleaner, air conditioners, washing machines, TVsets, stereos, telephone sets, bathtubs, taps, running water, toilet bowls, construction materials and so on. Is it going to be enough to start successful forecasting of the conception of the ‘smart house of the future’?
Probably yes, as the common sense tells us that we can’t make a plausible forecast of development of vacs if we don’t study all the systems which contact them and make a ‘technozenosis’ i.e. are in the same area of use.
Actually, in our system of sciences of engineering creativity there haven’t been created any models of cooperative evolutions just to have less or more formalized image of the main phenomenon of development in the models of technozenosis «техноценозов» [17]. I mean the transfer of technologies. We don’t even have information on how, according to what scripts the principles change принципы [18] [20], the principles which machines work on, and it’s an important area of knowledge, as important as ZRTS which regards useful properties.
8. Conclusion
I’d like to conclude this article with one more hypothesis which says that ‘classical TRIZ’ all new ‘TRIZ-like’ innovative subjects G3:ID [21], DE (Directed Evolution by Boris Zlotin [22]), the teory of ‘Harmful machines by Vasily Lenyashin [4], (despite their differences in targets and models, can be united by means of developing a central supposition which can be named ‘the main theorem of innovations’
The main theorem of innovations in the terms of engineering philosophy
People develop ‘machines’ (artificial systems of technological and informational nature) in the direction of reduction of drawbacks on one hand and increasing profits from the number of consumers (sales) on the other hand, if we use the algorithm of choosing the cheapest resources to reach this goal. The ‘drawback’ is a variable depending on the time, so the process of developing these machine – goods is eternal.
The picture with the see-saw, on the left ‘consumer’ , on the right ‘manufacturer’.
The purpose of the consumer is to satisfy any of his 8 needs at lowest price.
The purpose of the manufacturer is to get the maximal profit from the act of satisfaction of the needs of the consumer.
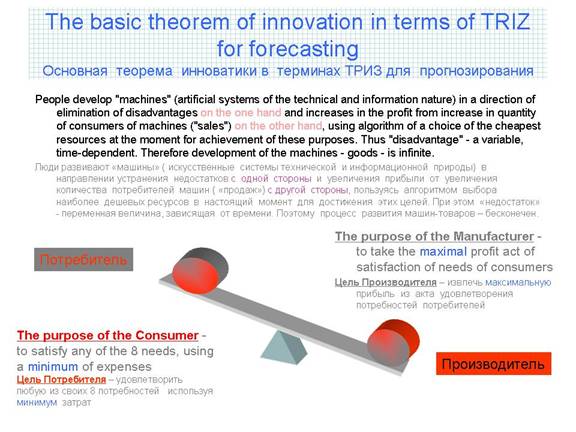
The diagram is taken from [15]
As I see it, classical TRIZ preferred the left side, all the modern triz-subjects are more concerned about the right side.
But we cant take away one side of the coin and leave only the other side, as all in the world follow the important dialectical ancient Chinese principle of Yin-Yan.
Sincerely yours, Yury Danilovsky
Sources
[1] Диверсионный анализ. Обзор. Ю. Даниловский
[2] ИСПОЛНЕНИЕ ПРОГНОЗОВ А. Кынин
[3] Поль Валери http://test.enigma.uran.ru/e-books/book_djvu/adamar/adamar.html
[4] "Вредная система" Использование этого понятия в современной ТРИЗ В.Леняшин, Россия, Хё Джун Ким, Южная Корея
[5] ОБЗОР СОВРЕМЕННЫХ МЕТОДИК СРАВНЕНИЯ КОНКУРИРУЮЩИХ СИСТЕМ ПРИ РАЗРАБОТКЕ НОВЫХ ПРОДУКТОВ Пустов Л.Ю.s
[6] Убить противоречие Ольга Рубан
[8] коллекция примеров по ЗРТС. Ю.Даниловский
[11] прикладная диалектика. Альбом. Ю.Даниловсский
[12] КОНСТРУКЦИИ И ТЕХНОЛОГИИ: ЕДИНАЯ МЕТОДИКА РАНЖИРОВАНИЯ ФУНКЦИЙ И СВЕРТЫВАНИЯ ЭЛЕМЕНТОВ Б. М. Аксельрод
[13] Объединение типа «старые и молодые». Альбом примеров. Ю.Даниловский
[14] ИСТОРИЯ РАЗРАБОТКИ ЗАКОНОВ РАЗВИТИЯ ТЕХНИЧЕСКИХ СИСТЕМ
© Владимир Петров. Тель-Авив, 2002
TRIZ-Isr@bigfoot.com текст приведен по рукописи
© 2002 by Vladimir Petrov
[15] 36 ВМ ( тренинг) альбом примеров. Ю.Даниловский
[16] Понятие Инновационной Безопасности. Альбом. Ю.Даниловский
[18] Сайт Ю.Мурашковского и М.Рубина ТЕММ
[21] Сайт компании Алгоритм и G3:ID
[22] Boris Zlotin and Alla Zusman: DIRECTED EVOLUTION: Philosophy, Theory and Practice. Ideation International Inc., 2001, 103 pages
In the pencil on the picture below the same approach is used: the lead has many colors but regular structure of a lead is changed into chaotic. This results in the fact that a drawn line changes colors without turning a pencil and this happens unpredictably.
From the point of view of HM model and diversion on the base of LDTS these can be taken like this: permanence of line color which a pencil leaves is declared* a drawback. In the format of “machine” we understand that this is conditioned by the presence of one working head. LDTS distinguishes the following line of development: mono – bi – poly system. Sometimes in this trend a new condition can be added. This is new “mono system”. Diversion in relation to a declared* drawback in the form of line color permanence is built in this very sequence: mono lead is replaced by poly lead in the variant of regular structure as in the upper pencil or it is changed into chaotic as in the pencil below.
HM – color permanence is broken on the level of operation with working head of useful machine (pencil lead) which was used on the phase “use”.
At the same time one more HM was studied. This machine was on the phase: purchase – sale.
The reduce or regularity of pencil sale made by a certain factory can be declared a drawback. Drawback can be paraphrased in the following way: absence of surprising option we have aleady discussed in the previous review. Diversion is an addition of a surprising option. The field of diversion application is working head of useful machine. Mechanism of diversion is based on LDTS in the form of a famous trend use mono – bi – poly complicated.
Logical illusion we spoke about in the previous review resulted in the fact that poly system created in the working head in the form of combination of colors in one lead is also a monosystem.
From LDTS point of view transmits along mono – bi – poly line is naturally traditional. New solution that enters the contradiction with usual direction of speculations demonstrates transmit mono – mono, or to be more exact mono – new mono because lead integrity hasn’t been changed and it saved its evolutionary condition - monolith.
However the concept of transmit to logical illusion itself is not a strictly determined dogma. You mustn’t take it as an imperative. The example with a pencil which leaves gibbous inscriptions illustrates agreement with traditional canons of LDTS line of speculations.
Dimension of result (line on the paper surface) – dimension 2 is declared a drawback and think that the answer to the drawback is dimension 3 in accordance with the trend: point – line – plane – volume.
So we make a diversion in relation to HM – flat image on a traditional script: change of aggregate condition of working head substance. This a famous consequence or tend: hard body – liquid – gas – phase transmits – complicated combined condition – plasma. In the working head of a pencil we replace “hard body” into “complicated combined condition”. Substance of a working head in a new solution is glue which in a closed condition is liquid and in the air it hardens in some time and acquires characteristic “hard body”.
And again we can speak about combination of two HM of different nature simultaneously because we discuss the appearance of surprising option.
In the glue you write little metal particle – sparkles are added and they make writing sparkling. The first HM in this example is a flat line; the second one is absence of surprising option.
All these examples of HM combination illustrate again productivity of Lenyashin model approach about taking a drawback as a machine. The note* near phrases “declare a drawback” I used many times is made to emphasize that drawback is a category both objective and subjective. Nobody considered permanence of line color a drawback before offering it to the market. The appearance of such a pencil realize the mechanism: demand breeds supply, which coexists with the mechanism: supply breeds demand.
Example:
After pen invention it was positioned as an easy procedure of entering the market for a long time, as a pen capable to write under water. This is the example of the mechanism “demand breeds supply” on the base of surprising potion appearance. Were there objective reasons for the appearance of a pen instead of usual parkers? They were. Passenger aviation appeared and an ink pen made a blot on the shirt because of change in atmospheric pressure during the flight.
Can we take the impossibility of writing under water of a parker as a drawback? We can if we consider it subjective.
The idea of a pen is 120 years. In 1888 John Load suggested the idea of a pen. I’ll notice the fact that absence of an eraser for a pen was quite an objective drawback at least for 60 years. In 40th of last century brothers Joseph Laslo and George Biro suggested to the market, practically simultaneously, a pen we accustomed to. In 2000 new pens with a special writing substance appeared. You can erase this substance with a thing that looks like eraser. And again somebody used mechanism “demand breeds supply” and a surprising option.
All explanation part of description of these examples can seem to a reader a theological exercise in interpretations. This is not exactly so. The matter is that thinking engineering creativity interests can be figuratively compared to polynuclear processor where one part operates the categories of engineering philosophy of the level of generalizations high enough: recourse, contradiction, principles, dualism and etc.
Another part makes some operations on parallel on the level of specific machine qualities: dynamism, variants of aggregate condition of a substance of working head, classification of movement kinds, combinations, use of this or that market scripts: technogenic mimicry and use of surprising option and etc.